- #1
freakywarlock
- 4
- 0
Hi,
I am working on RC OScillator Circuit, but i had problems with adjusting frequency. I can adjust frequency but it effects amplitude too (amplitude is changing while adjusting frequency), how can i separate these two variables ? I mean, when I am adjusting frequency, I want to amplitude remains same, and also for amplitude too. By the way I am using this circuit : (Ignore the Op-amp Circuit, it is converting sinusoidal wave into square wave.)
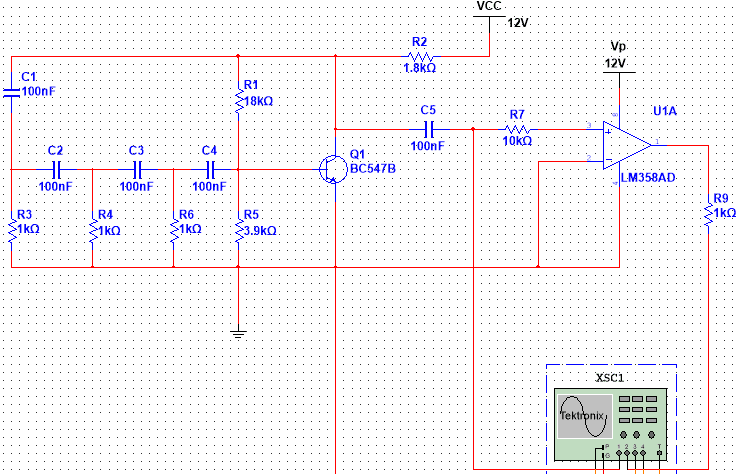
I am working on RC OScillator Circuit, but i had problems with adjusting frequency. I can adjust frequency but it effects amplitude too (amplitude is changing while adjusting frequency), how can i separate these two variables ? I mean, when I am adjusting frequency, I want to amplitude remains same, and also for amplitude too. By the way I am using this circuit : (Ignore the Op-amp Circuit, it is converting sinusoidal wave into square wave.)