- #1
Happiness
- 679
- 30
The rays of light from a moving source are tilted towards the direction of the source's motion. It is as if light emitted by a moving object is concentrated conically, towards its direction of motion. This effect is called relativistic beaming.
For example, if a source is emitting light vertically downwards when it is at rest, then when it is moving to the right, the light ray from the moving source is tilted to the right, such that the ray makes an angle less than ##90^\circ## to the rightwards-pointing horizontal axis.
If we visualise the source to be emitting photons vertically downwards, then since the source is moving to the right, the second photon emitted should be displaced to the right from the first one. Then if we join up these photons with a line to form a light ray, then we would get a light ray that is pointing downwards but tilted to the left, like this:
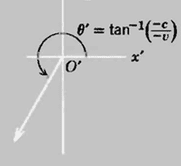
This photon model (or equivalently, bird poop dropping at regular intervals) produces the opposite prediction from the observations of relativistic aberration. What is wrong with the bird-poop-dropping model?
For example, if a source is emitting light vertically downwards when it is at rest, then when it is moving to the right, the light ray from the moving source is tilted to the right, such that the ray makes an angle less than ##90^\circ## to the rightwards-pointing horizontal axis.
If we visualise the source to be emitting photons vertically downwards, then since the source is moving to the right, the second photon emitted should be displaced to the right from the first one. Then if we join up these photons with a line to form a light ray, then we would get a light ray that is pointing downwards but tilted to the left, like this:
This photon model (or equivalently, bird poop dropping at regular intervals) produces the opposite prediction from the observations of relativistic aberration. What is wrong with the bird-poop-dropping model?