You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
AI Thread Summary
To maintain an output voltage of 4V while removing resistors, the analysis indicates that removing resistor Z is feasible without altering the voltage across the remaining components. The calculated EMF of the cell is 6V, and combining resistors X and Y results in a total resistance of 3000 ohms. To achieve the desired output, the current must be adjusted from 2mA to 1.33mA. This adjustment confirms that removing resistor Z will not affect the output voltage. Therefore, the solution suggests that Z can be safely removed.
Physics news on Phys.org
rl.bhat
Homework Helper
- 4,432
- 10
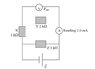
From the given data, find the emf of the cell.
To get the same output, what to do with X and Z so that the current in Y is 2 mA ?
To get the same output, what to do with X and Z so that the current in Y is 2 mA ?
xcvxcvvc
- 392
- 0
Think about it this way: If you combined X and Y in series, you'd have two parallel resistors. If you removed one of those parallel resistors(Z!), the voltage across and the current through the other parallel resistor does not change.
TyErd
- 297
- 0
okay EMF I calculated to be 6V, and then I combined X and Y to make another 3000ohm resistor and because I want output to be 4V, then that would mean current has to change from 2mA to 1.33mA correct? which means i can remove Resistor Z. Is that right I am not sure
Here we know that if block B is going to move up or just be at the verge of moving up
##Mg \sin \theta ## will act downwards and maximum static friction will act downwards ## \mu Mg \cos \theta ##
Now what im confused by is how will we know " how quickly" block B reaches its maximum static friction value without any numbers, the suggested solution says that when block A is at its maximum extension, then block B will start to move up but with a certain set of values couldn't block A reach...
TL;DR Summary: Find Electric field due to charges between 2 parallel infinite planes using Gauss law at any point
Here's the diagram. We have a uniform p (rho) density of charges between 2 infinite planes in the cartesian coordinates system. I used a cube of thickness a that spans from z=-a/2 to z=a/2 as a Gaussian surface, each side of the cube has area A.
I know that the field depends only on z since there is translational invariance in x and y directions because the planes are...
Figure 1 Overall Structure Diagram
Figure 2: Top view of the piston when it is cylindrical
A circular opening is created at a height of 5 meters above the water surface. Inside this opening is a sleeve-type piston with a cross-sectional area of 1 square meter. The piston is pulled to the right at a constant speed. The pulling force is(Figure 2): F = ρshg = 1000 × 1 × 5 × 10 = 50,000 N.
Figure 3: Modifying the structure to incorporate a fixed internal piston
When I modify the piston...
Similar threads
- Replies
- 9
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 6K
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 946
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 60
- Views
- 10K
Hot Threads
-
Torque biomechanics
- Started by Naucus
- Replies: 6
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
Recent Insights
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 11
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 3
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 1
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 105
- General Math
-
Insights Why Vector Spaces Explain The World: A Historical Perspective
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 0
- General Math