cellery
- 6
- 0
Being a rather novice engineer, I'm having trouble coming up with a solution to this problem. I think it's a rather simple problem with just a slightly complex twist (unsteady flow).
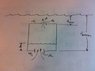
There's a tank submerged in water a certain depth (pictured). The tank has a known volume and contain a known initial volumes of water and air. At a certain instant, a hole is opened in the top of the tank such that air rushes out the top and water rushes in the bottom.
I realize this is an unsteady flow problem since the tank has a finite volume and it fills with water, displacing the air, but I think if someone could help me understand how to calculate the water flow velocity into the bottom and the air flow velocity out from the top just at the instant the top is opened (i.e., consider it steady for just that instant), I can do the rest of the unsteady analysis. If someone is willing to help model this as an unsteady problem, that's great too.
I know: the areas of the openings at the top and the bottom, the depths below the surface of the top and bottom of the tank (and therefore the hydrostatic pressures at each), the volume of the tank, the initial volumes of water and air in the tank, the initial height of water in the tank, and flow loss factors for the bottom and top holes.
I've been modeling the differential pressure across the holes like so:
deltaP = (1/2)*density*V_bottom^2*k_bottom, likewise for the top, where k is the flow loss factor associated with the shape of the hole.
I think that's about it. Any help would be appreciated. Thanks
There's a tank submerged in water a certain depth (pictured). The tank has a known volume and contain a known initial volumes of water and air. At a certain instant, a hole is opened in the top of the tank such that air rushes out the top and water rushes in the bottom.
I realize this is an unsteady flow problem since the tank has a finite volume and it fills with water, displacing the air, but I think if someone could help me understand how to calculate the water flow velocity into the bottom and the air flow velocity out from the top just at the instant the top is opened (i.e., consider it steady for just that instant), I can do the rest of the unsteady analysis. If someone is willing to help model this as an unsteady problem, that's great too.
I know: the areas of the openings at the top and the bottom, the depths below the surface of the top and bottom of the tank (and therefore the hydrostatic pressures at each), the volume of the tank, the initial volumes of water and air in the tank, the initial height of water in the tank, and flow loss factors for the bottom and top holes.
I've been modeling the differential pressure across the holes like so:
deltaP = (1/2)*density*V_bottom^2*k_bottom, likewise for the top, where k is the flow loss factor associated with the shape of the hole.
I think that's about it. Any help would be appreciated. Thanks