Buzz Bloom
Gold Member
- 2,517
- 465
From time to time I come across some text in a Wikipedia article that is quite misleading to a naive reader. The following is an example:
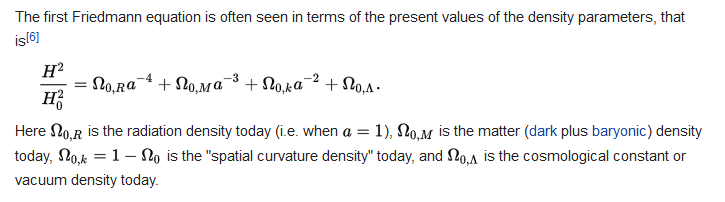
The problem is that the sign of Ω0,k is backwards. That is the sign is positive for a universe with negative (hyperbolic) curvature, and negative for a universe with positive (hyperspherical) curvature. In particular, the variable k was previously introduced with a description that k=+1 corresponds to positive curvature, and k=-1 corresponds to negative curvature.
I am hopeful that some knowledgeable PFs participant will edit the article to make this clear to a naive reader. There are several reasons why I do not feel competent to do this myself.
The problem is that the sign of Ω0,k is backwards. That is the sign is positive for a universe with negative (hyperbolic) curvature, and negative for a universe with positive (hyperspherical) curvature. In particular, the variable k was previously introduced with a description that k=+1 corresponds to positive curvature, and k=-1 corresponds to negative curvature.
I am hopeful that some knowledgeable PFs participant will edit the article to make this clear to a naive reader. There are several reasons why I do not feel competent to do this myself.