- #1
KiyoEtAlice
- 16
- 0
URGENT! T and U paradox
I'm really confused about how I should do this problem and this is urgent so if anyone can help, it would be very much appreaciated. Thanks.
T and U Bar paradox (This is my assigned homework, it is an edit of question 6-5 from a textbook called Spacetime Physics, it's one of my teacher's collection so I don't know anything more):
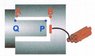
A U shaped structure made of the strongest steel contains a detonator switch connected by wire to one metric ton of explosive TNT. A T-shaped structure made of the same strong steel fits inside U, with the long arm of T not quite long enough to reach the detonator switch when the two collide. Therefore there will be no explosion.
But, look at the same situation in the rest frame of the T structure . In this frame the arm of the T has its rest length, while the two arms of the U-structure are Lorentz-contracted. Therefore the arm of the T will certainly strike the detonator switch and there will be an awful explosion.
Q: ==> Make two spacetime diagrams (the bigger the better) representing the motion of the objects in the T frame and in the U frame. Take the relative speech to be 87% of the speed of light --then the contraction is half of the rest length. Label the front and back of the T structure P and Q respectively and A and B the front and back of the U structure. Determine from your diagram whether there will be an explosion or not. And explain Why your diagram gives your answer.
**I've attached the image of this paradox that I found on the net to make things clear (and yes the image is right). Please help me out on the drawings and explanation, I'm not really sure how to do it. Note: the diagram is not the solution, it is just another version of the diagram that goes with the question.
Well, I am completely blank at this. I know how it should be like, and I know that it wouldn't explode.
Thanks!
Homework Statement
I'm really confused about how I should do this problem and this is urgent so if anyone can help, it would be very much appreaciated. Thanks.
T and U Bar paradox (This is my assigned homework, it is an edit of question 6-5 from a textbook called Spacetime Physics, it's one of my teacher's collection so I don't know anything more):
A U shaped structure made of the strongest steel contains a detonator switch connected by wire to one metric ton of explosive TNT. A T-shaped structure made of the same strong steel fits inside U, with the long arm of T not quite long enough to reach the detonator switch when the two collide. Therefore there will be no explosion.
But, look at the same situation in the rest frame of the T structure . In this frame the arm of the T has its rest length, while the two arms of the U-structure are Lorentz-contracted. Therefore the arm of the T will certainly strike the detonator switch and there will be an awful explosion.
Q: ==> Make two spacetime diagrams (the bigger the better) representing the motion of the objects in the T frame and in the U frame. Take the relative speech to be 87% of the speed of light --then the contraction is half of the rest length. Label the front and back of the T structure P and Q respectively and A and B the front and back of the U structure. Determine from your diagram whether there will be an explosion or not. And explain Why your diagram gives your answer.
Homework Equations
**I've attached the image of this paradox that I found on the net to make things clear (and yes the image is right). Please help me out on the drawings and explanation, I'm not really sure how to do it. Note: the diagram is not the solution, it is just another version of the diagram that goes with the question.
The Attempt at a Solution
Well, I am completely blank at this. I know how it should be like, and I know that it wouldn't explode.
Thanks!