feynman1
- 435
- 29
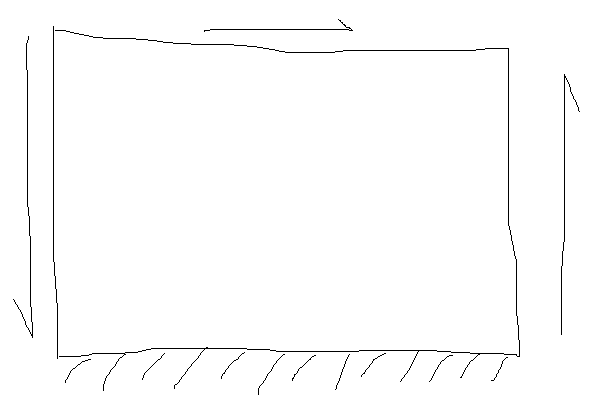
A rectangle (plane strain/stress) is sheared on 3 edges (bottom fixed) so that it becomes a parallelogram. In theory this is pure shear and should undergo uniform deformation throughout the domain. The FEA result for this pure shear loading still shows stress/strain concentration on the bottom corners. Is that normal and how to get rid of them?