- #1
KT KIM
- 24
- 0
Studying Lagrangian mechanics starting from D'Alembert's principle.
I just ran into this.
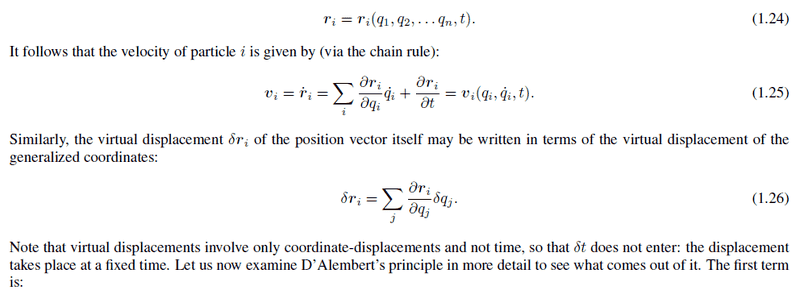
Why virtual displacement doesn't contain time t for it's coordinates
What does that mean 'take place at a fixed time'?
I just ran into this.
Why virtual displacement doesn't contain time t for it's coordinates
What does that mean 'take place at a fixed time'?