Franklie001
- 49
- 7
Summary:: Having the following dates:
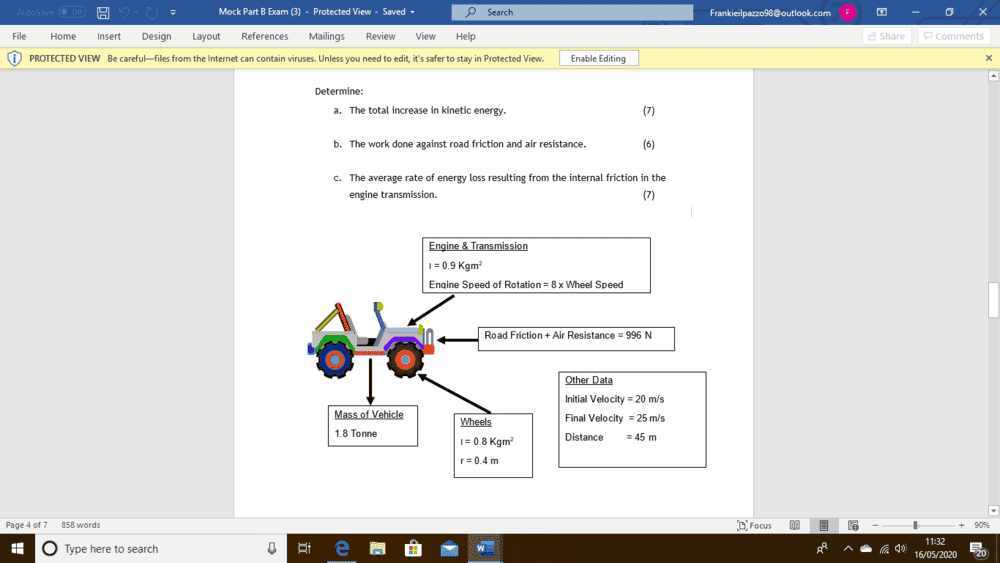
The discussion focuses on calculating the average rate of energy loss due to internal friction in a motor vehicle's engine transmission. Key data includes a vehicle mass of 1.8 tonnes, an effective moment of inertia for the engine and transmission of 0.9 kgm², and an average indicated power of 160 kW. The kinetic energy increase during acceleration from 20 m/s to 25 m/s is calculated to be 245,250 J, while the work done against road friction and air resistance is 44,820 N*m. The participants emphasize the importance of showing work for homework help and provide guidance on converting energy to power.
PREREQUISITESStudents studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and energy dynamics, as well as engineers involved in automotive design and performance analysis.

Sure, but on my screen I can't read it. What is the problem statement, and what are the given data?Franklie001 said:question posted

BvU said:
That's strange: I found something different. Can you post your work ?Franklie001 said:245.25*10^3J
 . Hold on...
. Hold on... ! Finally reproduced your a) result
! Finally reproduced your a) result Apparently you already know what is the right result.Franklie001 said:still can't get the right result.
I suppose the wheels can be ignored, or else they mean 'including the wheels'...Franklie001 said:The average rate of energy loss resulting from the internal friction in the engine transmission.
It is used to add kinetic energy (a), to overcome road friction and air resistance (b) and the remainder is (c).Franklie001 said:During this time the average indicated power of the engine is 160kW
$$ 1 \ {\sf W} = 1 \ {\sf J/s}$$Franklie001 said:How do I convert joules to kW?