- #1
lazyaditya
- 176
- 7
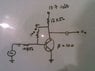
The circuit is shown below and i am asked to find out the voltage gain A(v)
Beta = 100 and Vcc = 13.7 volts Common emitter configuration.
Voltage Gain is equal to the ratio of output voltage to input voltage .
Don't know how to proceed as there wasn't any v(i) or v(o) given in the equation, how should i start ?
Beta = 100 and Vcc = 13.7 volts Common emitter configuration.
Voltage Gain is equal to the ratio of output voltage to input voltage .
The Attempt at a Solution
Don't know how to proceed as there wasn't any v(i) or v(o) given in the equation, how should i start ?