Questions999
- 151
- 0
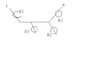
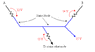
I am solving a VERY complicated exercise and I have this part that I don't understand.The image posted is a very big simplification of a part of the exercise.I have to find the potential between A and B.My question : Are the 15 Volt and the 13 Volt in the picture involved in the calculation?
I know I have to calculate the potential using Kirch.law btw.
I know I have to calculate the potential using Kirch.law btw.