vktsn0303
- 30
- 0
While reading a textbook on viscous flows, I came across the following interpretation of an equation:
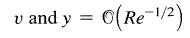
where, v is the vertical component of the free stream velocity and y is the vertical distance from the surface of a solid and Re is the reynolds number.
Can someone please help me understand what this interpretation means?
Thanks in advance
where, v is the vertical component of the free stream velocity and y is the vertical distance from the surface of a solid and Re is the reynolds number.
Can someone please help me understand what this interpretation means?
Thanks in advance
