- #1
blue.flake
- 11
- 1
Member advised to use the homework template for posts in the homework sections of PF.
Two identical tuning forks vibrate at 256 Hz. One of them is then loaded with a drop of wax, after which 6 beats/s are heard. The period of the loaded tuning fork is?
So, as the uploaded pictures shows, I did solve the problem, but I'm not sure why the f1 frequency is bigger than f2. I mean how can I be sure which one should I subtract from the other?
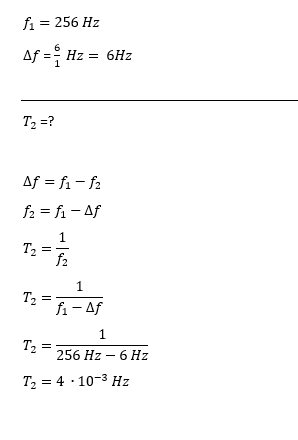
edit: yeah i just noticed i messed up the unit for the period, I'm sorry..
So, as the uploaded pictures shows, I did solve the problem, but I'm not sure why the f1 frequency is bigger than f2. I mean how can I be sure which one should I subtract from the other?
edit: yeah i just noticed i messed up the unit for the period, I'm sorry..