You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
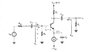
Why Are RL and RC Considered Parallel in Common Emitter Amplifier AC Analysis?
- Thread starter exis
- Start date
AI Thread Summary
In AC analysis of a common emitter amplifier, RL (load resistor) and RC (collector resistor) are considered to be in parallel due to the low impedance path created between ground and Vcc. This assumption is valid because coupling capacitors, like Cc2, are treated as shorts at AC frequencies. Consequently, any changes in collector current (IC) due to input signal (isig) affect both resistors simultaneously. This parallel configuration simplifies the calculation of output voltage (Vo) in response to AC signals. Understanding this concept is crucial for accurate AC analysis in amplifier design.
Physics news on Phys.org
skeptic2
- 1,776
- 60
In AC analysis there should be a very low impedance between ground and Vcc. Likewise Cc2 is assumed to be a short, thus RL and Rc are in parallel.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 17
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 25
- Views
- 9K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 2K
Hot Threads
-
Engineering Why is my output current so low in this Transconductance Amplifier cell?
- Started by arhzz
- Replies: 13
- Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
LTspice: Implementing a Single Balanced BJT Mixer
- Started by SumDood_
- Replies: 17
- Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
Max water pressure allowable on solar panels
- Started by ethanesh
- Replies: 16
- Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
Spiral scissor lift statics
- Started by carlcla
- Replies: 4
- Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
Recent Insights
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 7
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 0
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 1
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 91
- General Math
-
Insights Why Vector Spaces Explain The World: A Historical Perspective
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 0
- General Math