SUMMARY
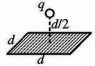
The discussion centers on calculating the electric flux through a square surface due to a point charge located above it. The correct expression for the electric flux is derived using Gauss' law, specifically \(\Phi = \frac{q_{enc}}{\epsilon_0}\). The participants clarify that the integral of the electric field \(E\) over the surface area \(dA\) must be considered, and due to symmetry, the flux through each face of an enclosing cube can be uniformly calculated. The consensus indicates that the answer is \( \frac{2q}{\epsilon_0 d} \), confirming the importance of integrating the electric field across the surface.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Gauss' law in electrostatics
- Familiarity with electric field concepts and calculations
- Knowledge of surface integrals in vector calculus
- Basic principles of symmetry in physics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of Gauss' law in various geometries
- Learn how to perform surface integrals in electromagnetism
- Explore the concept of electric fields generated by point charges
- Investigate the implications of symmetry in electric flux calculations
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, particularly those studying electromagnetism, educators teaching electric field concepts, and anyone preparing for exams involving electrostatics and electric flux calculations.