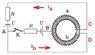
The coil cannot be broken into 2 separate coils!
To explain why briefly, that's because there is magnetic flux linkage between the upper half and the below half of the coil, i.e. B-field by one half penetrates into the other half. If they were 2 separate coils, their magnetic fields would be separate.
Okay, then why B-field by one half can penerate into the other half? That's because of the iron core. One important characteristic of the coil of whose rounds are linked by ONE iron core: The magnetic flux through each round is the same and is the combined result of B-field by all rounds.
In this problem, there is a difference between the current of the upper half i_a and that of the lower half i_b, so I suggest you should go back to the most fundamental.
For an isolated inductor (i.e. there is no other B-field penetrating into it or any external wire connecting to the middle of it like in this problem), current through the inductor cannot change immediately: di/dt = 0; but the reason behind that is the magnetic flux through the inductor cannot change immediately, and since the inductor is isolated, magnetic flux ~ i, and hence, i cannot change immediately.
(1): Therefore, for this problem, the magnetic flux \Phi through the whole coil cannot change immediately.
(2): Suppose that the iron core is uniform and linear. Plus the fact that the 2 halves are geometrically identical, we have B-field by each half is: B_a = ki_a and B_b = ki_b. Notice that the proportional coefficient k is the same for the two halves, as they are identical.
(3): We have \Phi \propto (B_a+B_b). Hence: \Phi \propto ki_a+ki_b \propto i_a + i_b. Notice that conventional directions of both currents are the same (see picture), and because of that, we have \Phi \propto (B_a+B_b); otherwise, it would be \Phi \propto B_a - B_b.
From (1), i_a+i_b cannot change immediately. Right before K is closed: i_a+i_b = 2I_0. Thus, right after K is closed: i_a + i_b = 2I_0. Notice that the sum is 2I_0 but not I_0 (as initially, right before K is closed, i_a = I_0 and i_b = I_0).
(4): As the magnetic flux through each round is the same (because of the iron core) and the two halves are identical and thus have the same number of rounds, the induced emf's on both halves are the same. Therefore: U_{BC} = U_{DB}. Notice that U_{BC} \neq U_{BD}, as when we say the magnetic flux through each round is the same, we implicitly understand that the magnetic flux goes through each round in the same direction.
(5): Write down Kirchhoff equations and solve

P.S.: A note on the separation of the coils. Personally, I think the inductor and all the equations involved like \Phi=Li are the creation of engineers, not scientists. Scientists only say: e_{induced} = -d\Phi /dt or e = - Ldi/dt at best, and that's all about Maxwell's equations. To go from that equation to v_L = Ldi/dt, we need some engineering model. So don't mistake that the equation u_L = Ldi/dt describes nature. It never does.
The equation e = -Ldi/dt is just like in the middle between science and engineering. It does assume a lot: the coil must be isolated, B-field is only concentrated inside the coil, there is no external B-field penetrating into the coil, etc. Such simplicity, though scientifically understandable, shows the sense of engineering. So a warn to those who want to go for engineering: sometimes simplicity in engineering may destroy your dream if there is a lack of rigorous science.
Yet, even scientists love simplicity