Constant acceleration Definition and 337 Threads
-
I
Gravity problem with non constant acceleration
Homework Statement You are a space traveler and you land on the surface of a new planet. You decide to drill a tunnel through the center of the planet to the opposite side of the planet. Your idea is to use this tunnel to easily transport rocks from your location to the opposite side of the...- inferno298
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Gravity
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
A powerboat, starting from rest, maintains a constant acceleration
Homework Statement A powerboat, starting from rest, maintains a constant acceleration. After a certain time t, its displacement and velocity are r and v. At time 2t, what would be its displacement and velocity, assuming the acceleration remains the same? a) 2r and 2v b) 2r and 4v c) 4r and...- hey123a
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Rest
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
What Constant Acceleration is Needed to Safely Pass an RV on a Two-Lane Highway?
Homework Statement You are driving along a two lane high way at 50 mph. An approaching car traveling 50 mph the other way is a quarter mile ahead of you. You wish to pass a 40 ft long RV going 40 mph with its rear bumper 70 ft in front of your front bumper. Your car is 12 ft long. What constant...- Kot
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Kinematics: Projectile Motion, Constant Acceleration
Please help. I think I may be over thinking this problem because it looks very simple. Homework Statement Determine the minimum initial velocity, v0, and corresponding angle, θ0 needed to kick the ball just over the 3m high fence. x = 6m y = 3m Homework Equations X: vx=v0x x = x0+v0xt v0x...- SammyLP250
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Kinematics Motion Projectile Projectile motion
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Constant acceleration, bike vs. car
Homework Statement Vroom, vroom! As soon as a traffic light turns green, a car speeds up from rest to 50.0 mi/h with constant acceleration 9.00 mi/h + s. In the adjoining bike lane, a cyclist speeds up from rest to 20.0 mi/h with constant acceleration 13.0 mi/h + s. Each vehicle maintains...- Feodalherren
- Thread
- Acceleration Bike Car Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Calculating Initial Velocity of an Electron with Constant Acceleration
Homework Statement I am about to start AS Level Physics and have been given some questions/problems to solve as introductory homework. However, I am stuck on one and cannot seem to get the answer specified as the correct one. An electron of mass 9.11x10-31kg is accelerated by a positive...- docbrown
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Seemingly easy mechanics problem (constant acceleration)
Homework Statement A jet plane comes in for a landing with a speed of 100 m/s, and its acceleration can have a maximum magnitude of 5.00 m/s^2 as it comes to rest. (a) From the instant the plane touches the runway, what is the minimum time interval needed before it can come to rest...- Feodalherren
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant acceleration Mechanics
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
High School Constant Acceleration Downwards
I remember being taught that, due to gravity, we are always accelerating downwards. But how do you explain it? Gravity is constant, and even if we are at rest, if I step on a scale I still get a weight of my mass X acceleration due to gravity. My forces vertically are balanced (me on the... -
Y
Graduate Thin rotating disc under constant acceleration.
In a different thread the Herglotz Noether theorem was brought up and it was mentioned that this theory implies it is impossible for a cylinder rotating about its vertical axis to remain Born rigid in a gravitational field even at constant altitude. This is an extension of the claim that a Born...- yuiop
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Disc Rotating Rotating disc
- Replies: 80
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
Constant Acceleration; Dynamics
Homework Statement Problem: Calculate the constant acceleration a in g’s which the catapult of an aircraft carrier must provide to produce a launch velocity of 188 mi/hr in a distance of 299 ft. Assume that the carrier is at anchor. Homework Equations V^2 = 2AD The Attempt at a...- allyfranken
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Dynamics
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Y
Constant acceleration in a straight line with variable distances
Homework Statement A particle which moves with a constant acceleration in a straight line passes through the point O, A and B in that order. If the distances OA and AB are 17 m and 35 m respectively and the particle takes the same amount of time , 3 seconds to travel each distance then...- yonewt
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Line Straight line Variable
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Graduate Constant acceleration from accelerated observer's perspective
First, an unnecessary short introduction of why I'm asking this question in the first place. Due to some doubts about a certain plot device in a science-fiction novel, I'm trying to figure out how long it would take to accelerate someone to, say, 50% of the speed of light under constant...- Whovian
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Perspective
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
Coefficient of kinetic friction and constant acceleration
Homework Statement A child's slide is flat, 5 meters long, and sloped down so that the top is 3 meters higher than the bottom. A child slides down, starting from rest, and has v = 6 m/s at the bottom. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction, μk is: Homework Equations F=ma f=μkFN...- addy899
- Thread
- Acceleration Coefficient Constant Constant acceleration Friction Kinetic Kinetic friction
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Constant Acceleration and Resolution of Forces
Homework Statement A block of concrete 5kg is initially at rest on a smooth (frictionless) horizontal surface. It is then pulled along by a constant force A, inclined at 45° from the horizontal. In the first 5 seconds of motion, the block moves a distance of 10m. A: Find the acceleration of...- FaraDazed
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Forces Resolution
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Graduate Maximal invariance group for constant acceleration?
Recently, over in the relativity forum, Micromass contributed a post: https://www.physicsforums.com/showpost.php?p=4168973&postcount=89 giving a proof that the most general coordinate transformation preserving the property of zero acceleration (i.e., maps straight lines to straight lines) is...- strangerep
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Group Invariance
- Replies: 0
- Forum: Calculus
-
B
Constant Acceleration of a skier Problem
Homework Statement A skier travels down a slope and leaves the ski track moving in the horizontal direction with a speed of 28 m/s. The landing falls off with a slope of 32 degrees. a.) How long is the skier airborne? ignoring air resistance b.) How far down the incline does the jumper...- bmb2009
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Kinematics of Constant acceleration word problem
So the problem is: a 1000 kg rocket is fired straight up, a 100 kg rocket is fired straight up with a constant acceleration for 16 seconds. It then stops accelerating and 20 seconds after launch reaches a height of 5100 m. Ignore air resistance. Find the acceleration of the rocket for the...- pistolpete333
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Kinematics Word problem
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
Using Equations for Constant Acceleration- Vertical Motion of a Bullet
Homework Statement A bullet is shot vertically into the air at a speed of 512 m/s. a) to what maximum height does the bullet go? b) how much time passes before the bullet stops rising? c) what is the velocity of the bullet after 60s? Homework Equations a) V2²=V1²+2ad b) a=...- L_0611
- Thread
- Acceleration Bullet Constant Constant acceleration Motion Vertical
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Constant acceleration problem to find the speed of a rocket
A rocket starts from rest and moves upward from the surface of the earth. For the first 10 of its motion, the vertical acceleration of the rocket is given by 2.60t, where the -direction is upward. What is the speed of the rocket when it is 240 above the surface of the earth? v = v0 + at...- mahrap
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Rocket Speed
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Graduate How does GR impact acceleration and reaching the speed of light?
I just watched a video whereby the man says that you could accelerate at a constant one g for 10 years and not reach the speed of light due to GR effects. I did a non-GR calculation and found that you would hit c at about one year. Could someone tell me specifically how GR affects this rate...- DiracPool
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Gr
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
F
Can a Motorbike Stop in Time to Avoid a Crash?
Homework Statement A motorbike is riding along a straight road at 25m/s when the rider suddenly notices that there is a broken down car in his way, 65 meters ahead. He immediately brakes giving the bike a constant deceleration of 5m/s^2. A. How far in front of the car does the biker come to a...- FaraDazed
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Graduate Non constant acceleration in gravitation field
To calculate the exact fall time of a mass, constant g is often used for a short distance traveled as for example in this paper: http://scitation.aip.org/getpdf/servlet/GetPDFServlet?filetype=pdf&id=AJPIAS000044000009000855000001&idtype=cvips&doi=10.1119/1.10277&prog=normal In this paper...- philipp2020
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Field Gravitation
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Mechanics
-
P
Kinematic Equations (Constant Acceleration)
Homework Statement The speed limit in a school zone is 40 km/h (about 25 mi/h). A driver traveling at this speed sees a child run onto the road 13m ahead of his car. He applies the brakes, and the car decelerates at a uniform rate of 8.0 m/s^2. If the driver's reaction time is 0.25 seconds...- Physics 134
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant acceleration Kinematic Kinematic equations
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Vi for Constant Acceleration Kinematics
So, there's a question that's been bugging me. If a ball is thrown upward to find out the height of a flag by timing when the ball passes the flag how do you find the height given that the ball passes the flag twice. When only time is given. So let's say t=5seconds and t=15 seconds I know...- diego1404
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Kinematics
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
How Far Does a Boulder Travel Rolling Downhill with Constant Acceleration?
[b]1. A boulder initially at rest rolls down a hill with an acceleration of 3.69m/s^2. If it accelerates for 7.72 seconds, how far will it move? [b]2. d=v0(initial velocity)t+.5at^2 [b]3. d=(0)(7.72)+.5(-9.8)(3.27)^2 -39.24+-52.4 -91.64m- Doraneli
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
O
A cart driven by a propeller with a constant acceleration
Homework Statement A cart is driven by a large propeller or fan, which can accelerate or decelerate the cart. The cart starts out at the position x = 0m, with an initial velocity of +4.85m/s and a constant acceleration due to the fan. The direction to the right is positive. The cart reaches a...- omc1
- Thread
- Acceleration Cart Constant Constant acceleration Propeller
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
High School Trouble Deriving a Constant Acceleration Formula
Q: How long does it take a car to cross a 30 m-wide intersection after the light turns green, if it accelerates from rest at a constant 2.00 m/s^2? Attempt: V=V0 + at; x-x0/t=v0+at; x-x0=v0+at^2; x=v0+x0+at^2; 30=0+0+2t^2; 15=t^2. The square root of 15 ended up being my final answer, when...- berenmacbowma
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration deriving Formula
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Mechanics
-
V
Constant acceleration muon problem
A muon enters a region with a speed of 5.00 x 10^6 m/s and then is slowed at a rate of 1.25 x 10^14 m/s^2. A) How far does the muon take to stop? After some research on the internet I have found an answer to the problem but that does not help me enough. Here is what I have found: Im suppose to...- vysero
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Muon
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Kinematics: Constant Acceleration
A badminton shuttle, or "birdie" is struck, giving it a horizontal velocity of 73m/s [W]. Air resistance causes a constant acceleration of 18m/s^2 [E]. Determine its velocity after 1.6s. I've used the equation V2=V1+ax x t V2= Final velocity V1=initial velocity A= Acceleration t=time...- SailorMoon01
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Kinematics
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
Motion with Constant Acceleration problem
Homework Statement A smaller propeller airplane can comfortably achieve a high enough speed to take off on a runway that is 1/4 mile long. A large, fully loaded passenger jet has about the same acceleration from rest, but needs to achieve twice the speed to take off. What is the minimum runway...- zerofaisal33
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Motion
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Super congfused about finding distance with constant acceleration
*confused A car speeding up from rest to constant accel. travels 100 meters in 6.04s. How far did it travel in the first 2.37 seconds? So I figure if I divide distance by time 100/6.04 it will give me the velocity 16.5m/s. And since distance = vt I would do d=15.6*2.37 which equals 37.03m but...- Butterfly30
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Elevator with constant acceleration
Homework Statement The Stratosphere Tower in Las Vegas is 1137 ft high. It takes 1 min, 20 s to ascend from the ground floor to the top of the tower using the high-speed elevator. The elevator starts and ends at rest. Assume that it maintains a constant upward acceleration until it reaches its...- cowmoo32
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Elevator
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
Derive a formula for motion with constant acceleration and constant deceleration
Homework Statement A subway train travels over a distance s in t seconds. it starts from rest and ends at rest. In the first part of its journey it moves with constant acceleration f and in the second part with constant deceleration r \, . Show that s \, = \, \frac {[\frac {fr} {f \...- LoA
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Deceleration Derive Formula Motion
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
Velocity under constant acceleration
The best leaper in the animal kingdom is the puma, which can jump to a height of 3.7 m when leaving the ground at an angle of 45°. With what speed must the animal leave the ground to reach that height? knowns: y=3.7 yo=0 Vo=0 V=want! I tried finding the velocity by using the equation...- nbroyle1
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Velocity
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
Calculating Constant Acceleration for a Cessna Aircraft Takeoff
A Cessna aircraft has a liftoff speed of 120 km/h. (a) What minimum constant acceleration does the aircraft require if it is to be airborne after a takeoff run of 250 m? (b) How long does it take the aircraft to become airborne? I tried using an equation for constant acceleration and...- nbroyle1
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
How long does it take for the car to pass the truck?
Homework Statement a car is behind a truck going 25m/s on the highway. the car's river looks for a chance to pass, guessing that his car can accelerate at 1.0m/s^2. he gauges that he has to cover the 20 meters length of the truck 10 meters clear room at the rear of the truck and 10 meters...- physicsguy69
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Motion
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Derivation of the Kinematic Equations
A car slows down from 23 m/s to rest in a distance of 85m. what was its acceleration, assumed constant? a=Δv/Δt x=1/2at^2 i don't know where to start- alexgraham
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Motion
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Physics question - Constant acceleration and distance travelled
physics question -- Constant acceleration and distance travelled an object is moving with a constant acceleration, if it travels a distance d during the first 2 seconds and an additional D in the next 2 seconds the ratio of D/d is? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 i don't understand exactly what...- physics.geeks
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Physics
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
Kinematics problem with constant acceleration
A ball is thrown downwards from a top of a 20m building with an initial velocity of 15m/s. What equation could be used to model its height? My answer: h (t) = -4.9t2-15t+20- livestrong136
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Kinematics Kinematics problem
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Finding the ratio of masses in constant acceleration motion
Homework Statement An engine provides a constant force F to a car of mass M that carries a box of mass m on the top of it. After traveling from rest with constant acceleration a1 for 20 seconds, the speed of the car becomes 40m/s and at that instant the box falls off the car. In the next 20...- Victorzaroni
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Motion Ratio
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Deriving constant acceleration formula
Since Ac = Dv/Dt (Ac being constant acceleration) I can isolate Dv and integrate both sides...did I derived the final equation correctly?http://img685.imageshack.us/img685/211/ssvvssvv.jpg Is that right?- Femme_physics
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration deriving Formula
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
Frictional Forces and Two dimensional constant acceleration problem
1. The floor of a railroad flatcar is loaded with loose crates having a coefficient of static friction of 0.36 with the floor. If the train is initially moving at a speed of 42 km/h, in how short a distance can the train be stopped at constant acceleration without causing the crates to slide...- Zach Lunch
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Forces
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Related to Constant acceleration
Homework Statement Suppose a child driving a go-cart is traveling 4m/s when she crosses a line 4m from her starting point. She continues with a steady acceleration of 0.4m/s^2 , until she crosses a mark 40m from the starting point. [FONT="Arial Black"]How long does it take for her to go from...- HelpMeHelpYou
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Constant acceleration of sports car
Homework Statement You are driving your new sports car at a velocity of 90km/hr , when you suddenly see a dog step into the road 50m ahead . You hit the breaks hard to get maximum deceleration of 7.5m/s² . Homework Equations i)How far will you go before stopping? ii)Can you...- HelpMeHelpYou
- Thread
- Acceleration Car Constant Constant acceleration Sports
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
How Far Does a Car Travel to Reach 4.61 m/s with Non-Constant Acceleration?
Homework Statement A car accelerates with the acceleration a(s)=k*s^n m/s^2 s= distance in m k = 5,8 n=0,7351 The car starts the acceleration from 0 m/s How far has the car traveled when it reaches the speed 4,61m/s? The Attempt at a Solution When i anti derivate one time i will get...- albert12345
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
What is the velocity of a car accelerating at a non-constant rate?
Homework Statement A car accelerates with a(s) = k·sn m/s2, from 0 m/s. What is the velocity of the car when s=1,3m? Homework Equations k = 7,96 och n = 0,454 The Attempt at a Solution I know I have to intergrate in some way, but I really don't know how to start? I don't have...- albert12345
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
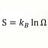
Proper Time : Constant Velocity Clock vs Constant Acceleration Clock
Homework Statement 3 clocks at to A clock on Earth B clock above Earth 4.66 * 1014 meters C clock above Earth 3.30 * 1013 meters B accelerates to .6 c and arrives at Earth when Earth clock reads 2.6 *106 sec = 30 days With velocity 1.8 *10^8 m/sec with gamma = .8 B clock reads 2.07 *...- Point Conception
- Thread
- Acceleration Clock Constant Constant acceleration Constant velocity Proper time Time Velocity
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Force and Constant Acceleration Problem
Homework Statement Sunjamming. A “sun yacht” is a spacecraft with a large sail that is pushed by sunlight. Although such a push is tiny in everyday circumstances, it can be large enough to send the spacecraft outward from the Sun on a cost-free but slow trip. Suppose that the spacecraft...- sb13
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Force
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
Forces of a Hammer Acting On a Nail With constant acceleration
Homework Statement A 4.9-N hammer head is stopped from an initial downward velocity of 3.2 m/s in a distance of 0.45 cm by a nail in a pine board. In addition to its weight, there is a 15-N downward force on the hammer head applied by the person using the hammer. Assume that the acceleration...- LoveHOPEpeace
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration Forces
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Constant Acceleration of jogging Problem
Homework Statement Al and Bert are jogging side by side on a trail in the woods at a speed of 0.75 m/s. Suddenly, Al sees the end of the trail 35 m ahead and decides to speed up to reach it. He accelerates at constant rate of 50 m/(s^2) while Bert continues on at a constant speed. (a) How...- JRangel42
- Thread
- Acceleration Constant Constant acceleration
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help