Marvin94
- 41
- 0
Hello everybody, I'm a little bit confused about two types of amplitude modulation. We distinguish here:
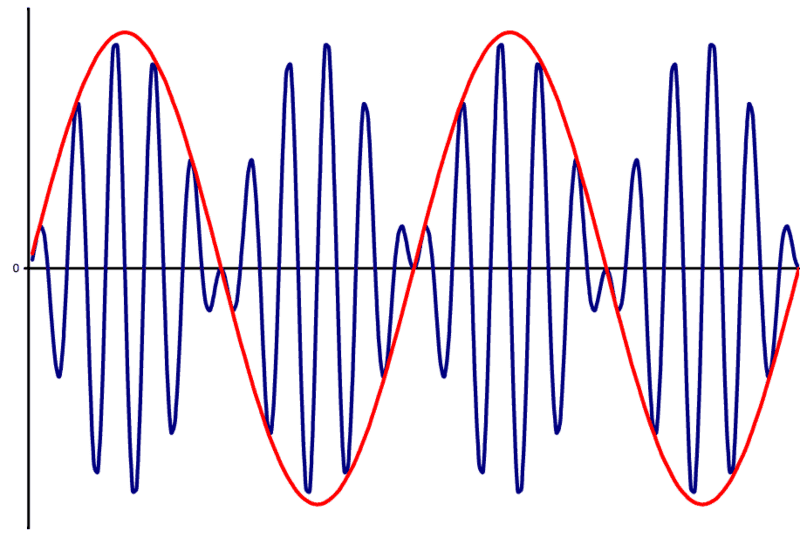
Case I : Amplitude Modulation with suppressed carrier (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double-sideband_suppressed-carrier_transmission):
 Case II : Amplitude modulation with carrier:
Case II : Amplitude modulation with carrier:
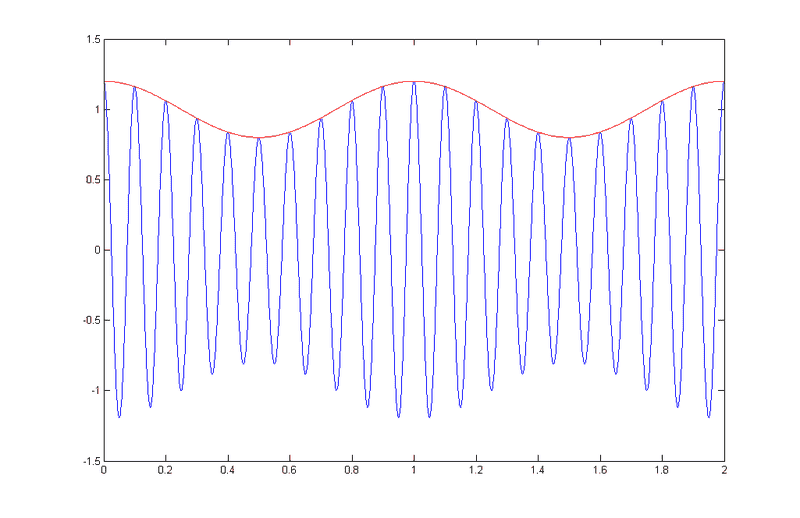
Now, it's not really clear to me the difference between the graphics above. More precisely, I have some questions about this topic:
1) How can be deduced from a signal plot which of the two cases is represented?
2) How can I understand the same from a matematical point of view? I mean, let's assume I have written down matematically the function of my signal. From this expression, how can I understand if the signal is modulated with carrier or with suppressed carrier?
3) Which operation should be done to obtain the Case I, and which operation to obtain the Case II ?
Thank you a lot in advance for any explanation!
Case I : Amplitude Modulation with suppressed carrier (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double-sideband_suppressed-carrier_transmission):
Now, it's not really clear to me the difference between the graphics above. More precisely, I have some questions about this topic:
1) How can be deduced from a signal plot which of the two cases is represented?
2) How can I understand the same from a matematical point of view? I mean, let's assume I have written down matematically the function of my signal. From this expression, how can I understand if the signal is modulated with carrier or with suppressed carrier?
3) Which operation should be done to obtain the Case I, and which operation to obtain the Case II ?
Thank you a lot in advance for any explanation!