- #1
lavankohsa
- 32
- 0
1. Consider the situation shown in figure. Initially the spring is unstretched when the system is released from rest. Assuming no friction in the pulley, find the maximum elongation of the spring.
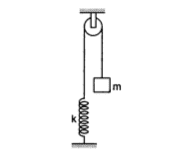
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B3FvaDRwJ2neQWtBU3JrazVTeEU/view?usp=sharing
I know that i can solve this problem by energy conservation.
mgx=1/2*k*x^2
so x=2mg/k
But i was thinking why can't we solve this problem by balancing of force.
mg=kx
so x=mg/k
because spring will stretched untll mg=kx
Please tell me where i am wrong in this[/B]
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B3FvaDRwJ2neQWtBU3JrazVTeEU/view?usp=sharing
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I know that i can solve this problem by energy conservation.
mgx=1/2*k*x^2
so x=2mg/k
But i was thinking why can't we solve this problem by balancing of force.
mg=kx
so x=mg/k
because spring will stretched untll mg=kx
Please tell me where i am wrong in this[/B]