smashbrohamme
- 97
- 1
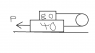
Knowing that friction equals 0.2 at all surfaces of contact, determine the magnitude of the force P required to move the 40kg plate B to the left. (Neglect Pulley Friction)
This is a statics problem asking how much force will it take to move block B which is 40kg...the problem is it has another block of 80kg sitting on top of it...and a pulley is connecting the 80kg block and the 40kg block.
the answer is 549N but I can't seem to find how to get it.
the 40kg block is on top of a friction plane that is 0.2...and a block is sitting on top of it that weighs 80kg. so I am assuming you have to count both frictions into the equation...
for the 40kg block I got Force to move it by itself is 152.96...and I am getting it takes 156.96 to move the 80kg block as well. so if you neglect the pulley's friction and just create a Tension of 156.96 I am only getting a force of 313.92N.
the picture is a lil funky but there is no angles to worry about.
This is a statics problem asking how much force will it take to move block B which is 40kg...the problem is it has another block of 80kg sitting on top of it...and a pulley is connecting the 80kg block and the 40kg block.
the answer is 549N but I can't seem to find how to get it.
the 40kg block is on top of a friction plane that is 0.2...and a block is sitting on top of it that weighs 80kg. so I am assuming you have to count both frictions into the equation...
for the 40kg block I got Force to move it by itself is 152.96...and I am getting it takes 156.96 to move the 80kg block as well. so if you neglect the pulley's friction and just create a Tension of 156.96 I am only getting a force of 313.92N.
the picture is a lil funky but there is no angles to worry about.