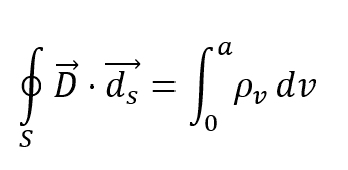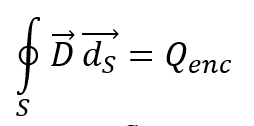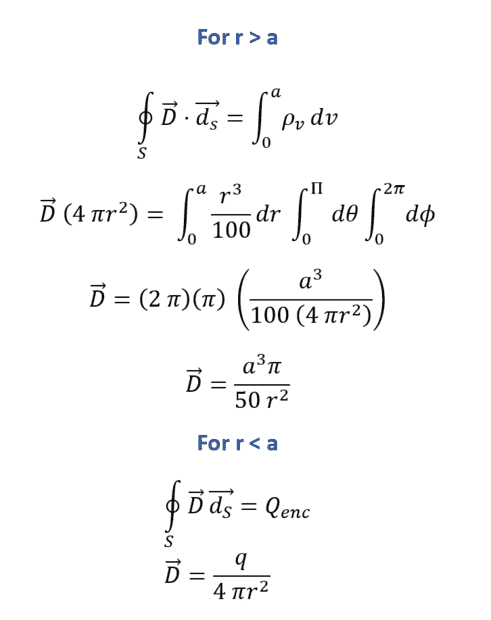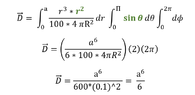Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating charge in the context of an electric field density that equals zero. Participants explore the mathematical integration involved in determining charge density over a sphere, addressing various assumptions and notation used in the calculations.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Some participants question whether the variable r is treated correctly as a constant or variable in the context of the sphere's radius.
- There is a discussion on the correct expression for the differential volume element dv in spherical coordinates.
- Participants debate the integration limits and whether certain terms should be treated as constants during integration.
- One participant suggests using different notations (r for the integration variable and R for a constant) to avoid confusion.
- There is a correction regarding the integral of r^3, with a participant stating it should be a^4 / 400 instead.
- Concerns are raised about the dimensions of expressions used in the calculations, emphasizing the need for consistent notation.
- A participant mentions obtaining a charge of -2.09e-8 C and discusses a discrepancy with another calculation that resulted in -2.09e-4 C.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the treatment of variables and constants in the integration process, leading to unresolved questions about the correct approach and notation. There is no consensus on the final calculations or methods used.
Contextual Notes
Limitations include potential confusion arising from the use of multiple variables (r and R) and the need for clarity in notation. Some mathematical steps remain unresolved, particularly regarding the integration process and the resulting charge calculations.