unscientific
- 1,728
- 13
Homework Statement
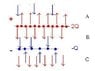
Given a capacitor, top plate with charge 2Q, bottom plate -Q: Find surface charge densities of all four surfaces and E-fields everywhere.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I start off with the general case of top plate having charge Q1, bottom plate Q2. Inner surfaces of capacitor get their charge densities distorted more. (Zero distortion when plates are very far away; equal charge distributed on inner and outer surfaces)
Inner and outer top surfaces charge density distorted by sigma, while bottom inner and outer surfaces distorted by gamma\sigma_1 = \frac{Q_1}{2A} - \delta, E_1 = \frac{1}{2\epsilon_0}(\frac{Q_1}{2A} - \delta)
\sigma_2 = \frac{Q_1}{2A} + \delta, E_2 = \frac{1}{2\epsilon_0}(\frac{Q1}{2A} + \delta)
\sigma_3 = -\frac{Q_2}{2A} - \gamma, E_3 = \frac{1}{2\epsilon_0}(-\frac{Q2}{2A} - \gamma)
\sigma_4 = -\frac{Q_2}{2A} + \gamma, E_4 = \frac{1}{2\epsilon_0}(-\frac{Q2}{2A} + \gamma)
Electric fields at regions
E_A = -E_1 - E_2 + E_3 + E_4 = \frac {1}{2\epsilon_0}(-\frac{Q_1}{A}-\frac{Q_2}{A})
E_B = E_1 - E_2 + E_3 + E_4 = \frac{1}{2\epsilon_0}(-2\delta -\frac{Q_2}{A}) = 0
E_C = E_1 + E_2 + E_3 + E_4 = \frac{1}{2\epsilon_0}(\frac{Q_1}{A}-\frac{Q_2}{A})
E_D = E_1 + E_2 -E_3 + E_4 = \frac{1}{2\epsilon_0}(\frac{Q_1}{A} + 2\gamma) = 0
E_E = E_1 + E_2 - E_3 - E_4 = \frac{1}{2\epsilon_0}(\frac{Q_1}{A} + \frac{Q_2}{A})
Answers
\sigma_1 = \frac{Q}{2A}, E_1 = \frac{Q}{4A\epsilon_0}
\sigma_2 = \frac{3Q}{2A}, E_2 = \frac{3Q}{4A\epsilon_0}
\sigma_3 = \frac{3Q}{2A}, E_3 = \frac{3Q}{4A\epsilon_0}
\sigma_4 = \frac{-Q}{2A}, E_4 = \frac{-Q}{4A\epsilon_0}
These answers are wrong, as the inner plates should have equal but opposite charge densities, the outer plates will have exactly same charge densities. I checked similar questions online.
I'm guesssing the charge densities should be (from top to bottom surfaces): +1/2, +3/2, -3/2, +1/2.
Last edited: