- #1
Kuma
- 134
- 0
Homework Statement
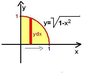
Here is the question
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
So converting to polars by x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ gives me r^5 in the inner integral
but how do you convert the ranges?
y goes from 0 to sqrt 1 - x^2, so that is just r, I could tell just by looking at it, but in a harder question how do you derive the range in terms of r? x goes from 0 to 1, but how do you convert that in terms of θ (an angle)?