- #1
r12214001
- 24
- 2
- Homework Statement
- What are the oxidation states of the cobalt ions?
- Relevant Equations
- N/A
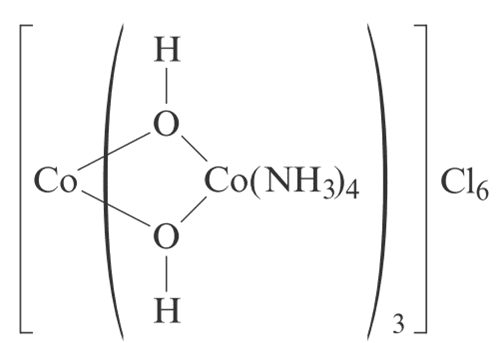
question fig:
solution manual:
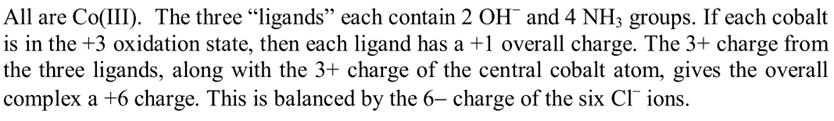
my solution:
oxidation state of central cobalt is +6 due to 6 oxygen surrounding it,The other cobalt is +2 due to 2 oxygen surrounding it with NH3 ligand which is no count for oxidation state.
solution manual:
my solution:
oxidation state of central cobalt is +6 due to 6 oxygen surrounding it,The other cobalt is +2 due to 2 oxygen surrounding it with NH3 ligand which is no count for oxidation state.