- #1
Trickster_00
- 6
- 0
Please use zoom function for better view.

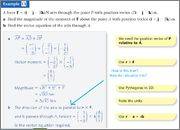
I'd highly appreciate it if you could also add a diagram on your explanation. Thanks!
I'd highly appreciate it if you could also add a diagram on your explanation. Thanks!