- #1
esoms
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
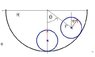
Suppose we have a skateboard half-pipe. The half-pipe has a radius R. We take a bicycle wheel of radius ρ and let it roll into the half-pipe. The wheel rolls without slipping ( and doesn't fall over, of course). Let Θ be the angle from the vertical to the line connecting the center of the half-pipe to the center of the bicycle wheel, and ø the angle the bicycle wheel has rotated.
(a) how are Θ,ø, R and ρ connected if the wheel rotates without slipping?
(b) Find the Lagrangian for the bicycle wheel. Use your answer from the previous part to simplify the Lagrangian.
Homework Equations
L= T-U
where L is the Lagrangian, T is the kinetic engery, and U is the potential energy
The Attempt at a Solution
I am very familiar with how to evaluate and set up lagrangians. However i am having trouble figuring out how to relate the variables for part a. I know the potential will be in the form of U=mgh and how to take partials to get the equations of motion.
It may be that i am confused about the angle Θ and where it is defined. something just isn't clicking. Any point in the right direction would be greatly appreciated. mostly i just need another mind to help me decipher how to do this. Once i get the relationships i should be good to continue on.
Thanks so much for all the help,
Eric