- #1
Karol
- 1,380
- 22
Homework Statement
Prove:
[tex]\cos\alpha\cdot\cos\alpha'+\cos\beta\cdot\cos\beta'+\cos\gamma\cdot\cos \gamma'=\cos\theta[/tex]
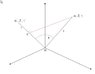
See drawing Snap1
Homework Equations
None
The Attempt at a Solution
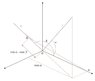
See drawing Snap2. i make the length of the lines 1 and 2 to equal one, for simplicity.
The projection of line 1 on one of the axes is cos(α).
##\cos\alpha\cdot\cos\beta## is the projection of line OA=cos(α) on line 2, which causes line AB to be perpendicular to line 2.
If i will make the same procedure for all 3 axes and add the 3 projections on line 2 i have to get, see Snap1, line OC which is ##1\cdot\cos\theta##, but i don't know how to do it.
The book from which i took this problem says i have to solve it from geometrical considerations.
Where can i find the proof to this problem?