gaobo9109
- 68
- 0
Homework Statement
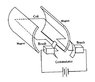
A simple DC motor consists of an armature placed between two poles of a magnet. The armature is rectangular and has dimensions of 90mm in breadth and 100mm in length. Magnetic flux density produced by the magnet is 0.5T. Number of turns of armature winding is 500. What is the change in magnetic flux when the armature is rotated through 360 degree
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
The answer I have arrived at is different from the answer provided.
My answer is as follow:
Change in magnetic flux = Area of the armature x magnetic flux density x 2
= 90mm x 100mm x 0.5T x 2
The answer provided is:
Change in magnetic flux = B x [Area swept in one revolution by each 100mm-side] x [2 sides]
= 0.5T x 2pi(90mm/2)(100mm) x 2
I have no idea how that answer is arrived at.