spitonem
- 4
- 0
I had this problem on my exam and I was pretty sure i knew what to do but it couldn't come up with the right answers.
I diagrammed the problem and showed the way i tried to solve it in blue. Can someone tell me where i went wrong?
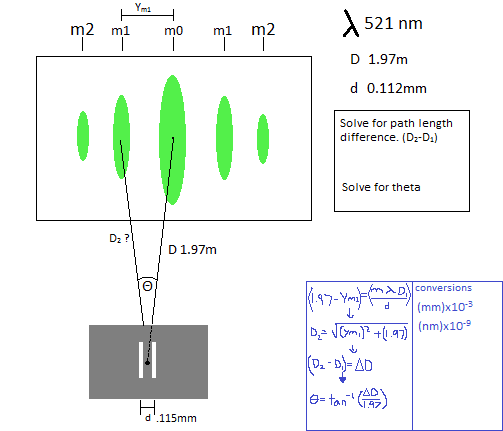
Basically i found the length the of the first maximum off the center. i used Pythagorean's theorem to find D2. Then subtracted the two distances to find the difference. I then took the arctan of that distance divided by D1.
I diagrammed the problem and showed the way i tried to solve it in blue. Can someone tell me where i went wrong?
Basically i found the length the of the first maximum off the center. i used Pythagorean's theorem to find D2. Then subtracted the two distances to find the difference. I then took the arctan of that distance divided by D1.