- #1
mtridge
- 1
- 0
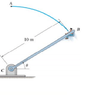
A man having the mass of 75 kg sits in the chair which
is pin-connected to the frame BC. If the man is always seated in
an upright position, determine the horizontal and vertical
reactions of the chair on the man at the instant theta = 45
degrees
. At this
instant he has a speed of 6 m/s, which is increasing at 0.5 m/s^2
if you can answer this great, but I am looking for someone who can more less give me a step by step to solve this. Thanks for the hlep
is pin-connected to the frame BC. If the man is always seated in
an upright position, determine the horizontal and vertical
reactions of the chair on the man at the instant theta = 45
degrees
. At this
instant he has a speed of 6 m/s, which is increasing at 0.5 m/s^2
if you can answer this great, but I am looking for someone who can more less give me a step by step to solve this. Thanks for the hlep