- #1
Luis Babboni
Hi people, me bother yo again!
I understand that relativity theory length contraction is the explanation of magnetics fields.
See the image:
https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/vuy69jhig3kni3n/densidadcargasencorriente.jpg?dl=0
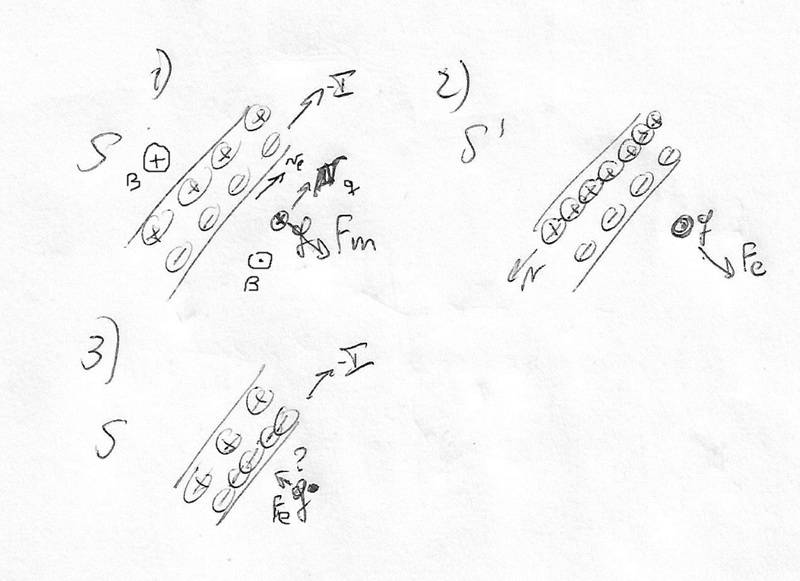
1) In the S system, if q is moving at the same velocity than the electrons that made the current, the -I current into a neutral wire produces a magnetic field B that make a force Fm on q.
2) It can be explained what happens in 1) from what happens in a system S´ that is moving at the same velocity than electrons and q. The length contraction of proton-proton distances made the wire not even more neutral so q, at rest in S´, feels an electric force Fe.
My question is why in S, as I show in 3) the moving of electrons do not result in length contraction of theire electron-electron distances making the wire not neutral and then an electric force Fe appears on q?
In this case I think I have the answer but not sure if it is correct and then I ask you about it:
Is cause "a neutral wire in S" is neutral because the main distances electron-electron in a frame where electrons are a rest is the one needed to make those distances are the same as proton-proton distances in a frame where protons are at rest?
Thanks!
PS: In the case my answer is correct, the trasient from neutral wire without currents to steady current in it, would be interesting in terms of relativity effects! I´m right?
I understand that relativity theory length contraction is the explanation of magnetics fields.
See the image:
https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/vuy69jhig3kni3n/densidadcargasencorriente.jpg?dl=0
1) In the S system, if q is moving at the same velocity than the electrons that made the current, the -I current into a neutral wire produces a magnetic field B that make a force Fm on q.
2) It can be explained what happens in 1) from what happens in a system S´ that is moving at the same velocity than electrons and q. The length contraction of proton-proton distances made the wire not even more neutral so q, at rest in S´, feels an electric force Fe.
My question is why in S, as I show in 3) the moving of electrons do not result in length contraction of theire electron-electron distances making the wire not neutral and then an electric force Fe appears on q?
In this case I think I have the answer but not sure if it is correct and then I ask you about it:
Is cause "a neutral wire in S" is neutral because the main distances electron-electron in a frame where electrons are a rest is the one needed to make those distances are the same as proton-proton distances in a frame where protons are at rest?
Thanks!
PS: In the case my answer is correct, the trasient from neutral wire without currents to steady current in it, would be interesting in terms of relativity effects! I´m right?

