- #1
Jamessamuel
- 45
- 0
I seem to have a fundamental misunderstanding of the principle here.
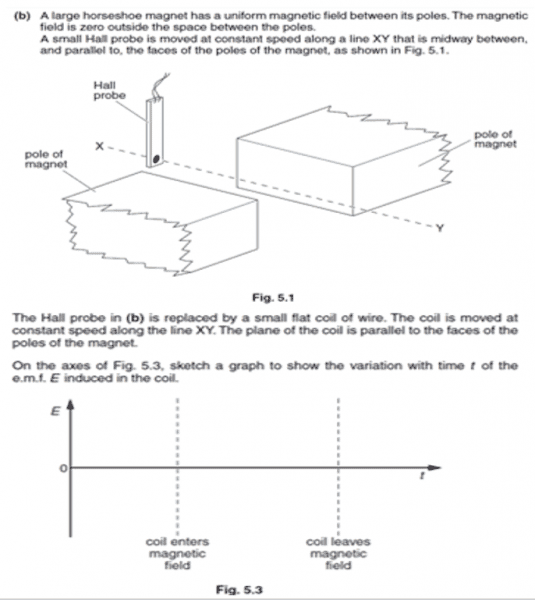
in the previous part it was required to sketch the graph for the hall probe. I knew since the speed was constant the field was cut at a constant rate hence a straight line was needed. However I did not understand why it dropped off sharply towards the end.
For the part shown in the image, I do not understand what is different about the coil graph from the probe graph. Surely the same logic applies, same rate of movement hence same EMF? Why would the coil be different?
in the previous part it was required to sketch the graph for the hall probe. I knew since the speed was constant the field was cut at a constant rate hence a straight line was needed. However I did not understand why it dropped off sharply towards the end.
For the part shown in the image, I do not understand what is different about the coil graph from the probe graph. Surely the same logic applies, same rate of movement hence same EMF? Why would the coil be different?
 ?)
?)