hamburgler
- 22
- 0
Holy current, how do you find the the current at each ammeter??
Find the current at each ammeter.
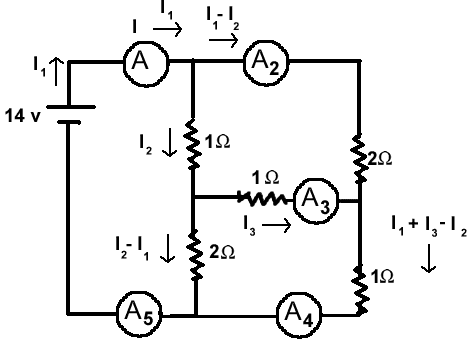
My solution
Someone told me to use
\sumE-\sumIR=0
to solve the system but they weren't sure.
But I cannot find anything about this on the internet and I'm freaking out!
Homework Statement
Find the current at each ammeter.
My solution
Someone told me to use
\sumE-\sumIR=0
to solve the system but they weren't sure.
But I cannot find anything about this on the internet and I'm freaking out!
Last edited:
