- #1
iVenky
- 212
- 12
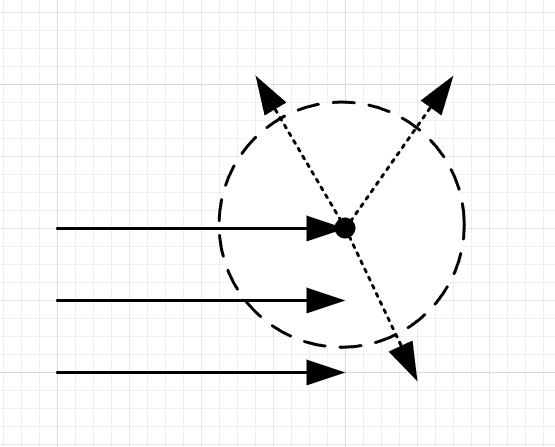
Let's assume a plane wave going in the x-direction. Going by Huygens' principle, each point on the wavefront should act like a source. If that's the case, wouldn't plane wavefront become spherical like shown below? I am so confused