chris2112
- 20
- 0
I was hoping someone could explain something I'm not quite understanding about light waves. I've researched many sources but I'm still not understanding exactly how they propagate.
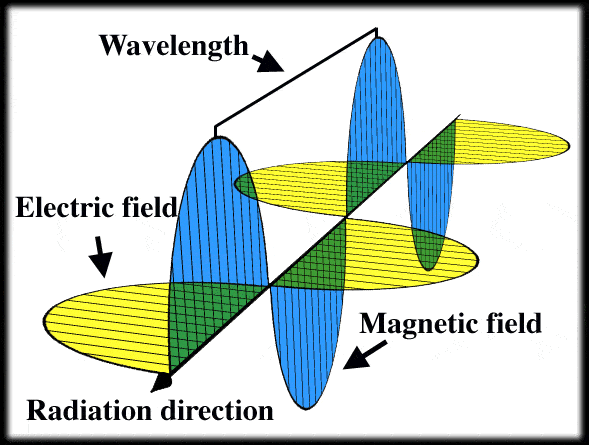
I understand that the electric field in any perpendicular section of the light ray creates a magnetic field perpendicular to it or vice versa, but I do not understand how they create each other in the direction of the ray to actually create it. I'm hoping someone can help me out with this. Thank you.
I understand that the electric field in any perpendicular section of the light ray creates a magnetic field perpendicular to it or vice versa, but I do not understand how they create each other in the direction of the ray to actually create it. I'm hoping someone can help me out with this. Thank you.