- #1
makerfeldt
- 6
- 0
Homework Statement
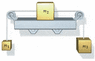
A box of mass m2 = 3.7 kg rests on a frictionless horizontal shelf and is attached by strings to boxes of masses m1 = 1.2 kg and m3 = 2.1 kg as shown below. Both pulleys are frictionless and massless. The system is released from rest. After it is released, find the following.
The Attempt at a Solution
I found the relevant forces of gravity to be 18.62 on m1, and 27.44 on m3, but I have little clue of where to go from there. Any idea would be greatly appreciated.