- #1
BIOS
- 9
- 0
Hello
The table below shows some kinetics values for two types of the GOD enzyme, the free and the immobilised.
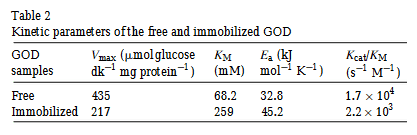
How can I comprehend what these values mean?
I want to know how many grams of substrate are 'converted' per sec per mg of enzyme.
I assume the substrate concentration plays role so I want to be able to incorporate that into the calculations.
Thanks!
The table below shows some kinetics values for two types of the GOD enzyme, the free and the immobilised.
How can I comprehend what these values mean?
I want to know how many grams of substrate are 'converted' per sec per mg of enzyme.
I assume the substrate concentration plays role so I want to be able to incorporate that into the calculations.
Thanks!