STENDEC
- 21
- 0
I've been using rotation matrices for quite some time now without fully grasping them. Whenever I tried to develop an intuitive understanding of...<br />
x' = x\cos\theta - y\sin\theta \\<br />
y' = x\sin\theta + y \cos\theta<br />... I failed and gave up. I've looked at numerous online texts and videos, but following the step-by-step explanations didn't lead to me seeing the whole picture as I had hoped.
Could someone explain to me (like I'm 5 years old), why -y\sin\theta and x\sin\theta are used to affect the value along the other axis?
Looking at the following picture (pardon the quality):
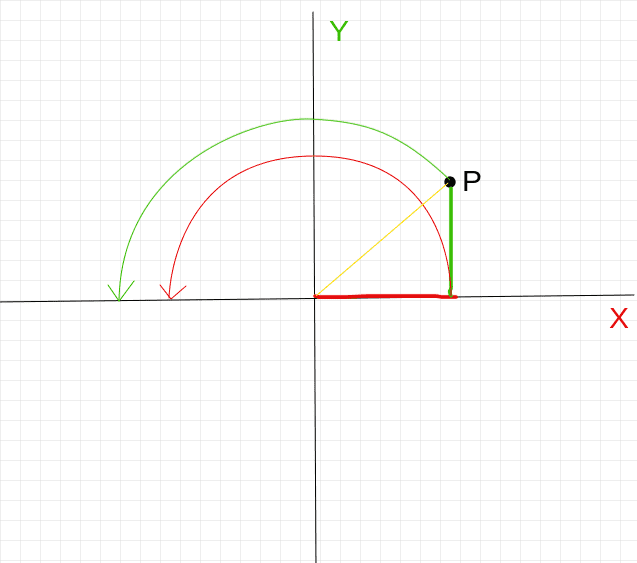
Is the contribution of y to x and vice versa there, to ensure that P maintains the correct distance to the origin, or is that a misguided simplification of mine? The yellow line cannot be sin + cos (Pythagorean theorem) yet I may combine these two to get x' and y'. Do you see where my gap in understanding lies? Is there a drawing that could clarify how these terms combine to give the correct value we observe? Algebraic proofs don't work with me I'm afraid, I need a geometric/visual explanation.
Could someone explain to me (like I'm 5 years old), why -y\sin\theta and x\sin\theta are used to affect the value along the other axis?
Looking at the following picture (pardon the quality):
Is the contribution of y to x and vice versa there, to ensure that P maintains the correct distance to the origin, or is that a misguided simplification of mine? The yellow line cannot be sin + cos (Pythagorean theorem) yet I may combine these two to get x' and y'. Do you see where my gap in understanding lies? Is there a drawing that could clarify how these terms combine to give the correct value we observe? Algebraic proofs don't work with me I'm afraid, I need a geometric/visual explanation.
Last edited: