Colnago
- 8
- 0
Hi guys,
Bit of a noob engineer here so looking for some guidance.
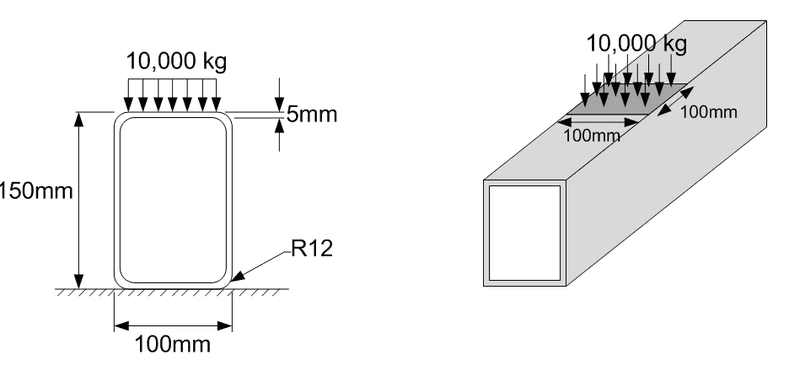
I'm designing a fixture which will be constructed from stainless steel rectangular tube as shown in the diagram. If I apply a 10,000kg weight over a 100mx100mm area how do I go about calculating the stress and ultimately safe working load?
The tube will be laid flat on the ground. Is this just a case of force/area? I'm struggling to find any textbook examples of loading applied to hollow sections in this way.
Thanks in advance!
Bit of a noob engineer here so looking for some guidance.
I'm designing a fixture which will be constructed from stainless steel rectangular tube as shown in the diagram. If I apply a 10,000kg weight over a 100mx100mm area how do I go about calculating the stress and ultimately safe working load?
The tube will be laid flat on the ground. Is this just a case of force/area? I'm struggling to find any textbook examples of loading applied to hollow sections in this way.
Thanks in advance!