- #1
ryanmcarthy
- 20
- 0
Please could you look over my questions and what answers I've come up with please, and see if I have done them correct?
Thanks a lot
Questions:

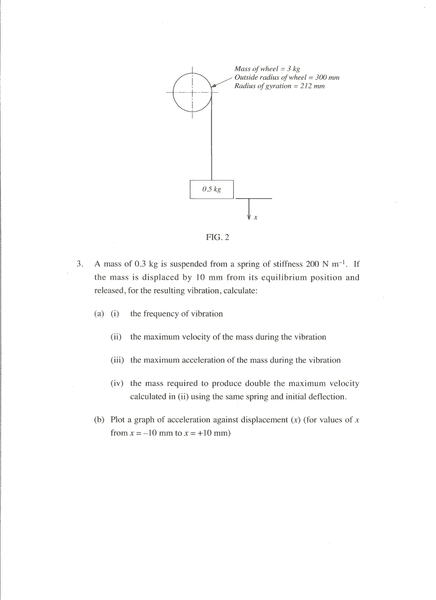
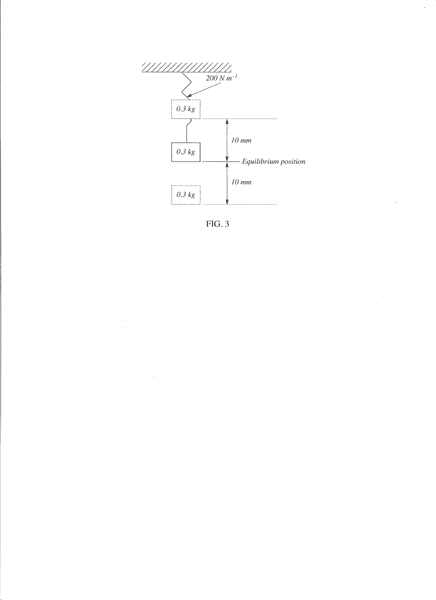
My Answers:
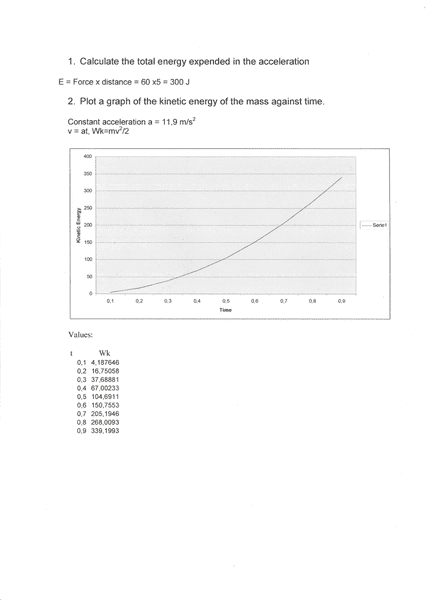
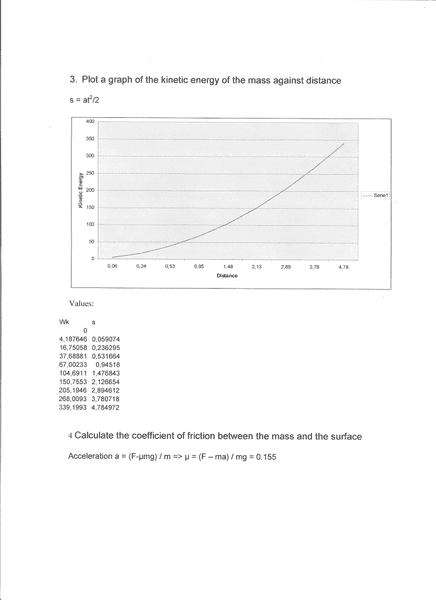


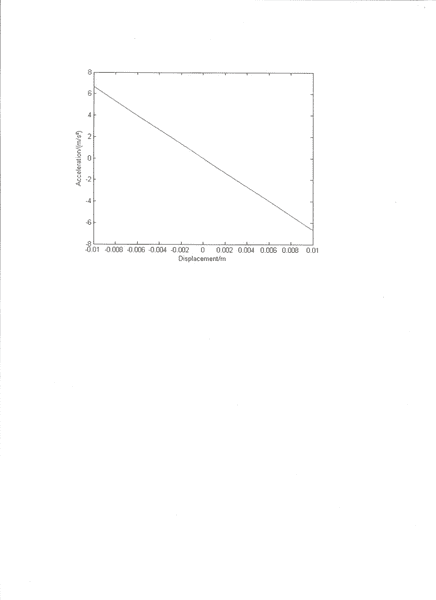
Thanks :)
Thanks a lot
Questions:
My Answers:
Thanks :)
Last edited: