- #1
Dan350
- 44
- 0
I think I on the rigth track, would you revise it please
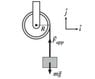
1. A motor is connected to a solid cylindrical drum with a radius of 0.6m and a mass of 52kg. A massless rope is attached to the drum and tied at the other end to a 38kg weight so the rope will wind onto the drum as it turns. The weigth is rising with an acceleration of 1.5m^2. See Image below.
a) What is the angular acceleration of the drum?
b) At the moment that the drum is rotating at ω=3.5rad/s what is the rate at which the motor is doing work?
2. Homework Equations
T=rfsinθ
T=Iα
F=ma
I=1/2mr^2
)
3. The Attempt at a Solution
For part a:
F=ma
Fapp-mg=ma
Fapp=m(a+g)
So I got the force of the acting on the system to use it in my torque so
T=rfsin(90)
T=257.64N
then we get the intertia of the drum, so I=1/2(52kg)(.6m^2)= 9.36kgm^2
so we can apply it
T/I=α
∴ 257.64/9.36= 27.52rad/s^2
attempt at b
W=∫Tdθ from θi to θf
∴
1/2Iωf^2-1/2Iωi^2
so plugin in values
1/2(9.36kgm^2)(3.5rad/s)^2
=57.33N
Am I correct? if not, would you tell me why and where am I wrong please.
Thank You
-Dan