- #1
Brett0
- 9
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- Linking closed container saturation vapour pressure and T-S diagram location
Hi all.,
Just hoping to get a better fundamental insight into a few things.
If we start with this:
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Kinetic/vappre.html
so we have a closed container at a given temperature, then we can find it's saturation pressure. All good so far.
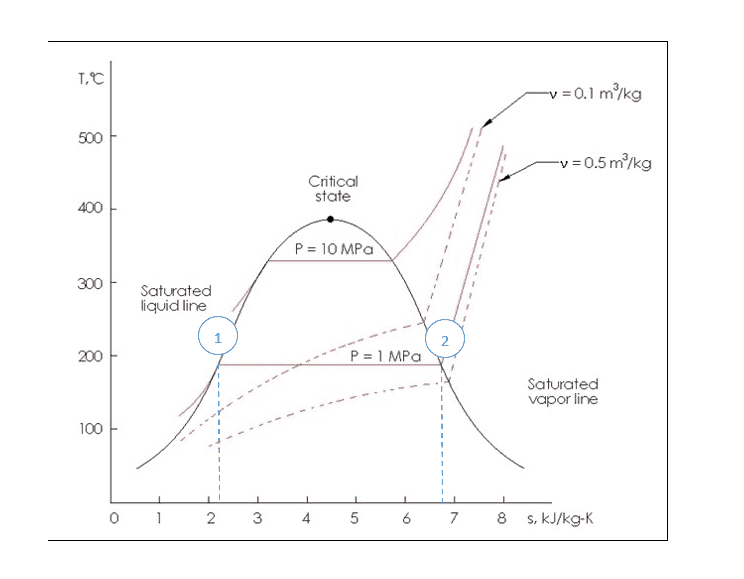
In the following figure ignore the actual value of 1MPa. Let's just assume that the P=1 MPa line is the hypothetical saturation pressure for our hypothetical substance at our hypothetical temperature as we defined above.
The question is where does that put us on the line between 1 and 2 as I've marked in blue circles in this picture? Anywhere along that line is at the same temperature and pressure. I suppose I'm looking to link this to the description given in the hyperphysics post.
Any help much appreciated.
Brett
Just hoping to get a better fundamental insight into a few things.
If we start with this:
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Kinetic/vappre.html
so we have a closed container at a given temperature, then we can find it's saturation pressure. All good so far.
In the following figure ignore the actual value of 1MPa. Let's just assume that the P=1 MPa line is the hypothetical saturation pressure for our hypothetical substance at our hypothetical temperature as we defined above.
The question is where does that put us on the line between 1 and 2 as I've marked in blue circles in this picture? Anywhere along that line is at the same temperature and pressure. I suppose I'm looking to link this to the description given in the hyperphysics post.
Any help much appreciated.
Brett