- #1
lionely
- 576
- 2
A narrow uniform glass tube contains air enclosed by a thread of mercury 15cm long.
When the tube is held vertically, with the closed end at the bottom,the air column is 20.0cm long, but when it is held horizontally the air column is 24.0cm long. Calculate the atmospheric pressure.
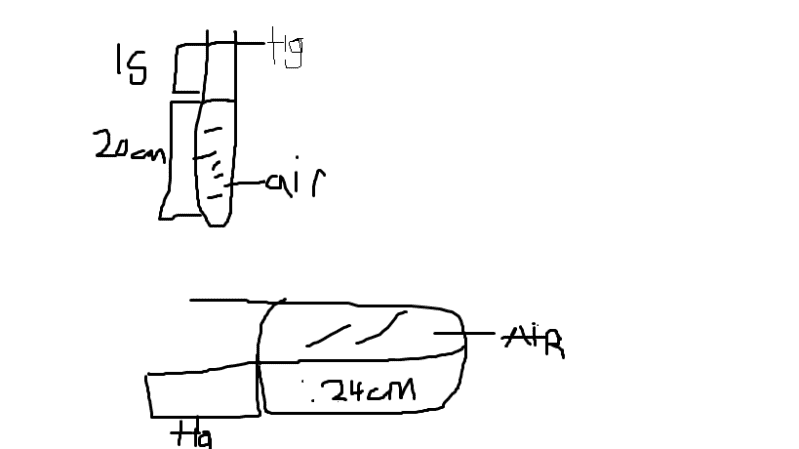
I drew a diagram I'm not sure if it's correct, I know that I'm supposed to subtract the mercury height from the barometric height but I don't get the correct answer. Please help me.
When the tube is held vertically, with the closed end at the bottom,the air column is 20.0cm long, but when it is held horizontally the air column is 24.0cm long. Calculate the atmospheric pressure.
I drew a diagram I'm not sure if it's correct, I know that I'm supposed to subtract the mercury height from the barometric height but I don't get the correct answer. Please help me.
