strugglin-physics
- 47
- 0
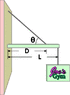
A shop sign weighing 206 N is supported by a uniform 132 N beam of length L = 1.89 m as shown in figure below.
The guy wire is connected D = 1.19 m from the backboard. Find the tension in the guy wire. Assume theta = 43.0 o
Find the horizontal force exerted by the hinge on the beam.
Find the vertical force exerted by the hinge on the beam. Use "up" as the positive direction.
I get T = -mg * 1/2L + T*L*sin(43) = T = mg/2sin(40)
Fx = Hx -T cos(43) = 0
Hx = T cos(43)
Fy = Hy -mg + Tsin(43) = 0
Hy = mg - Tsin(43)
But these are incorrect. Where did I go wrong?
The guy wire is connected D = 1.19 m from the backboard. Find the tension in the guy wire. Assume theta = 43.0 o
Find the horizontal force exerted by the hinge on the beam.
Find the vertical force exerted by the hinge on the beam. Use "up" as the positive direction.
I get T = -mg * 1/2L + T*L*sin(43) = T = mg/2sin(40)
Fx = Hx -T cos(43) = 0
Hx = T cos(43)
Fy = Hy -mg + Tsin(43) = 0
Hy = mg - Tsin(43)
But these are incorrect. Where did I go wrong?