- #1
Juniper7
- 19
- 0
Homework Statement
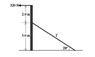
A uniform vertical beam of mass 40kg is acted on by a horizontal force of 520N at its top and is held, in the vertical position, by a cable as shown in the attached picture.
a) Calculate the tension in the cable
b) Determine the reaction forces acting on the beam by the ground
Homework Equations
F=T-mg
The Attempt at a Solution
I think I over simplified this:
∑Fx = Fcablecos28° - Fapplied force = 0
Fccos28° = Fa
Fc = 588.94N <---- answer to a)
∑Fy = Fcsin28° + mg - FN = 0
Fcsin28° + mg = FN
(588.94N)sin28° + (40kg)(9.81m/s2) = FN
FN = 668.49N <----- answer to b)
Thank you in advance for any help!