physixnot4me
- 27
- 0
This is the question I was given a homework assignment:
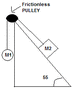
2) Two objects are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley. Draw a Free Body Diagram of both objects. If the inclide is frictionless and if m1= 2kg, m2=6kg and angle theta=55 degrees, find:
(a) the accelerations of the objects
(b) the tension in the string
(c) the speed of each object 2 sec after being released from rest.
**my question is: is the acceleration for both objects the same, just different directions?**
how do you incorporate the theta 55 degrees into this question?
2) Two objects are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley. Draw a Free Body Diagram of both objects. If the inclide is frictionless and if m1= 2kg, m2=6kg and angle theta=55 degrees, find:
(a) the accelerations of the objects
(b) the tension in the string
(c) the speed of each object 2 sec after being released from rest.
**my question is: is the acceleration for both objects the same, just different directions?**
how do you incorporate the theta 55 degrees into this question?