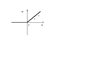- #1
shaiqbashir
- 106
- 0
Hi Guys:
My question is this
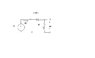
for the circuit in the 1st fig: sketch the transfer charcteristic "vo" versus "vI"
the answer of this question is the 2nd fig. but i want to know that what is the logic behind this sketch or in other words how we can draw such a sketch.
Thanks in advance
My question is this
for the circuit in the 1st fig: sketch the transfer charcteristic "vo" versus "vI"
the answer of this question is the 2nd fig. but i want to know that what is the logic behind this sketch or in other words how we can draw such a sketch.
Thanks in advance