- #1
1msm
- 8
- 0
Hello,
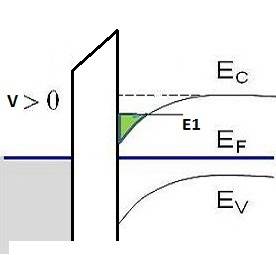
In a MOS capacitor or MIS after applying a voltage on the metal, the valence band and the conduction band bend downwards
(in the usual band diagram) when a positive voltage is applied. (p-type semiconductor).
When the voltage is large enough, electrons forms an inverse layer(green) with an energy level E1, as shown in below picture.
Now my question is,
How the electrons lost their energy by falling from higher conduction energy level (Ec) to lower inversion level E1.. ?
Thanks..
In a MOS capacitor or MIS after applying a voltage on the metal, the valence band and the conduction band bend downwards
(in the usual band diagram) when a positive voltage is applied. (p-type semiconductor).
When the voltage is large enough, electrons forms an inverse layer(green) with an energy level E1, as shown in below picture.
Now my question is,
How the electrons lost their energy by falling from higher conduction energy level (Ec) to lower inversion level E1.. ?
Thanks..