- #1
flughafen
- 2
- 0
- Homework Statement
- statistics
- Relevant Equations
- pmf
I am new to the topic so I do need your help here. Thanks in advance
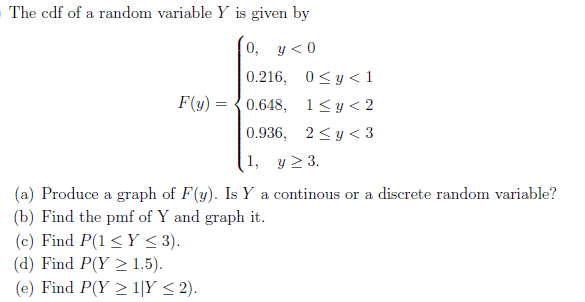
 !
!BvU said:Hello @flughafen,!
Unfortunately for you, PF requires an effort from you before we are allowed to assist. So: what have you got thus far ?
flughafen said:I haven't gotten much far yet. Just left it there, thinking that I could use the answer of this as base for other alike questions.
The PMF (Probability Mass Function) of a random variable Y is a function that assigns probabilities to each possible value of Y. It describes the probability distribution of Y and can be represented as a graph or a table.
The PMF of Y is used for discrete random variables, while the PDF (Probability Density Function) is used for continuous random variables. The PMF gives the probability of a specific value of Y occurring, while the PDF gives the probability of Y falling within a certain range of values.
The PMF of Y can be calculated by determining the probability of each possible value of Y using the formula P(Y=y) = number of outcomes where Y=y / total number of outcomes. This can be done using a table or a graph, depending on the distribution of Y.
The PMF of Y provides information about the probability distribution of Y. It tells us the likelihood of different values of Y occurring and can help us understand the characteristics and behavior of the random variable.
Yes, the PMF of Y can be used to calculate the expected value of Y, which is the average value that we would expect to obtain if we repeatedly sampled Y. The formula for calculating expected value using the PMF is E(Y) = Σ y * P(Y=y), where y represents each possible value of Y.