- #1
thomas19981
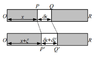
The figure below shows a section of a thin, elastic rod of density ##\rho##, cross sectional area ##A##, and modulus of elasticity ##E##.
By considering the net force acting on an element of the rod, derive the wave equation governing its longitudinal motion:
##\frac{\partial^2(\xi)}{\partial t^2}=\frac{E}{\rho}\frac{\partial^2(\xi)}{\partial x^2}##
where ##\xi## is the displacement of the medium from its equilibrium position.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
My solution is inserted as an image but I can't see where I'm going wrong with this question.
Many thanks in advance.